As technology evolves, so do the methods of cyberattacks, making traditional authentication vulnerable. This is where Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) steps in, offering an extra layer of defense. In this article, we delve into the synergy between MFA and RADIUS-enabled devices and software, exploring how this dynamic duo bolsters protection against modern security challenges and how to integrate multi-factor authentication for RADIUS.
1. What is RADIUS
In computer networking, RADIUS, or Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, is a protocol used to manage and secure user access to a network. It operates as a central authentication and authorization system, ensuring that only authorized users can connect to network resources. RADIUS facilitates user authentication by verifying usernames and passwords. It’s commonly employed in scenarios such as Wi-Fi access points, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), and other remote access systems.
RADIUS plays a vital role in enhancing network security by enabling administrators to control user access and monitor usage while maintaining a centralized and efficient authentication process. Integrating multi-factor authentication (MFA) can significantly strengthen this authentication process. Multi-factor authentication or two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second piece of information, such as a one-time code generated on a mobile device. In this article, we’ll explore why enhancing your RADIUS network security is crucial by implementing multi-factor authentication, and how to add MFA via RADIUS to elevate the security of network access.
Distinguishing Between RADIUS Protocol, RADIUS Server, and RADIUS Client
Let’s break down the RADIUS puzzle for a clearer picture:
- The RADIUS protocol stands at the core of this system, serving as the communication framework that enables secure data exchange between RADIUS servers and clients. It employs a client-server model where the RADIUS client, often a networking device seeking authentication for its users, sends access requests to the RADIUS server. This protocol ensures the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information during transmission, safeguarding user credentials from potential threats.
- RADIUS servers, on the other hand, serve as the guardians of authentication. These specialized servers store user credentials and related information in a centralized database. When a RADIUS client forwards an access request, the RADIUS server validates the user’s credentials and responds with an acceptance or denial message. This centralized approach streamlines user management by allowing administrators to enforce policies and access controls uniformly, reducing administrative overhead and enhancing security.
- Meanwhile, RADIUS clients encompass devices that require user authentication for accessing network resources. These clients can range from Wi-Fi access points and switches to VPN gateways. Upon receiving a user’s access request, the RADIUS client relays the credentials to the RADIUS server for validation. If successful, the RADIUS client grants the user access to the requested services; if not, access is denied. This mechanism ensures that only authorized users can utilize network resources, bolstering the overall security posture.
Understanding RADIUS and Its Vulnerabilities
While RADIUS serves as a stalwart guardian of network access, it’s not immune to vulnerabilities. The RADIUS protocol lacks encryption for the packets exchanged between the client and server, except for the password. While the password is encrypted, the overall security of RADIUS relies heavily on its proper implementation. However, even with flawless execution, if a hacker only needs to overcome a password to breach an account, the vulnerability remains significant.
Traditional single-factor authentication, relying solely on usernames and passwords, can be a weak link. Cyber threats, from phishing to brute-force attacks, exploit this vulnerability, potentially leading to unauthorized access and data breaches. Hackers are adept at cracking weak passwords or tricking users into revealing their credentials. Furthermore, compromised devices and insider threats can pose significant risks.
As technology advances, so do the tactics of malicious actors. It’s clear that a robust authentication framework is imperative to thwart these vulnerabilities and bolster network security. This is where Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) steps in, providing an additional layer of protection that addresses the shortcomings of single-factor methods.
2. The Power of Multi-Factor Authentication for RADIUS
When it comes to the RADIUS protocol, one of the most effective ways to enhance security is through the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
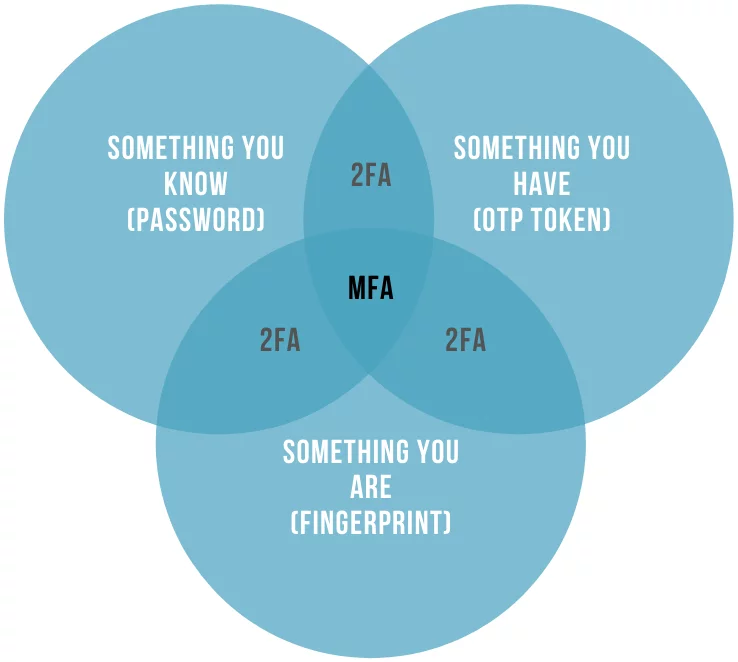
Multi-factor authentication, or MFA, goes beyond traditional username and password verification by requiring users to provide at least two or more different types of authentication factors. These factors fall into three main categories:
- Something You Know: This is the most common authentication factor, involving information that only the user should know, such as a password or PIN. While passwords remain a fundamental part of MFA, it’s crucial to ensure they are strong, unique, and regularly updated to prevent unauthorized access.
- Something You Have: This factor relies on possession of a physical item that is uniquely associated with the user. Examples include security tokens or mobile devices that receive one-time codes. These devices generate or provide access to time-sensitive codes that must be presented during the authentication process, adding an extra layer of security.
- Something You Are: This factor involves biometric data unique to each individual, such as fingerprints, retinal scans, or facial recognition. Biometric authentication is increasingly popular due to its reliability and resistance to traditional hacking methods.
By incorporating multiple authentication factors into the RADIUS protocol, organizations can significantly enhance security. Even if malicious actors manage to obtain one factor (e.g., a password), they would still need the other factor(s) to gain access. This multi-tiered approach reduces the risk of unauthorized access, ensuring that sensitive data and network resources remain protected.
Furthermore, MFA aligns with industry standards and regulations, making it an essential component of a robust cybersecurity strategy. Compliance requirements in various sectors, including finance, healthcare, and government, often mandate the use of multi-factor authentication to safeguard sensitive information and maintain data integrity.
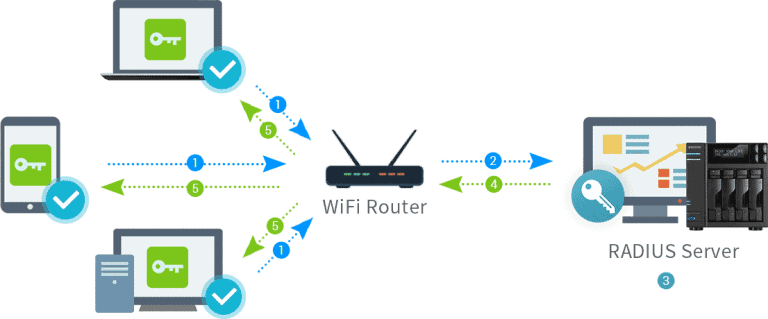
3. How Does MFA Work With RADIUS?
Integrating Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) with the RADIUS authentication protocol is a straightforward yet powerful way to fortify your network’s security. Here’s how this combination works:
- Authentication Request: When a user attempts to access a RADIUS-enabled device or service, they provide their credentials (typically a username and password) as the first authentication factor.
- RADIUS Server Connector: The RADIUS server, often implemented as a connector like the Protectimus RADIUS Server, comes into play. It acts as an intermediary, forwarding the user’s authentication request to the MFA server.
- MFA Authentication: The MFA server takes charge of the second authentication factor, which could be something the user possesses (e.g., a mobile app generating a one-time code) or something inherent to the user (e.g., a fingerprint scan).
- Two-Factor Verification: The MFA server validates both authentication factors. If both factors are correct, it sends an authorization response back to the RADIUS server connector.
- Access Granted or Denied: Based on the response from the MFA server, the RADIUS server connector makes the final call. If the MFA authentication is successful, the RADIUS server connector grants access to the user. If not, access is denied.
- Secure Access: With both authentication factors verified, the user gains access to the RADIUS-protected device or service. This two-factor verification significantly enhances security by ensuring that only authorized users with both the correct credentials and the second authentication factor can proceed.
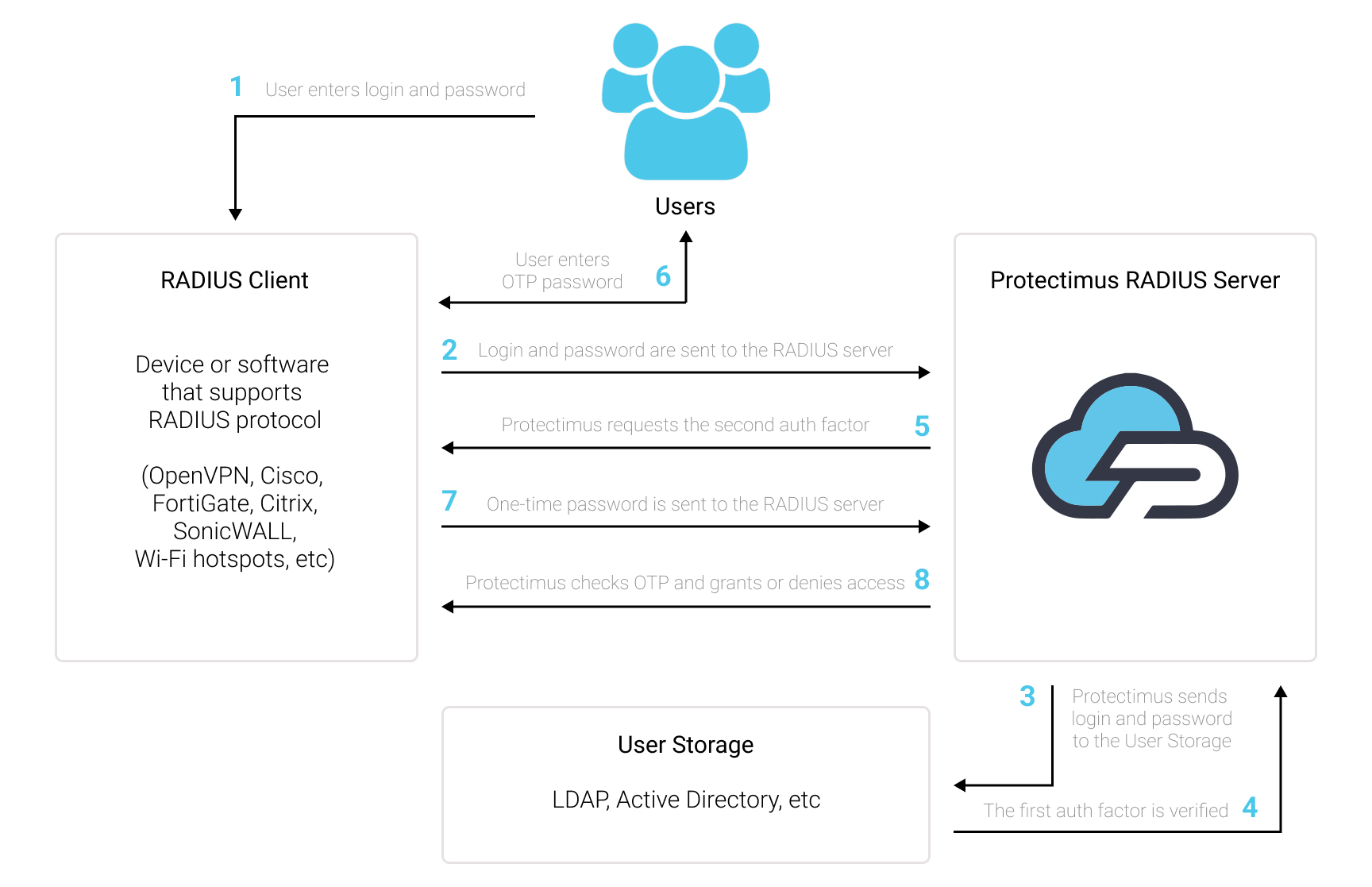
The key advantage of this approach is that it adds an extra layer of security without requiring significant changes to existing RADIUS-enabled systems. It seamlessly integrates the robustness of MFA with the familiarity of RADIUS, offering a robust solution to safeguard sensitive resources and data.
4. What RADIUS-Enabled Devices and Services Should I Protect with MFA
To maximize security within your network infrastructure, it’s essential to identify which RADIUS-enabled devices and services warrant the additional protection of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
- VPN Access: VPNs are often the gateway to an organization’s sensitive resources. Protecting VPN access with MFA ensures that only authorized individuals can establish secure connections.
- Wireless Networks: Wi-Fi access points and networks utilizing RADIUS for authentication benefit from MFA, preventing unauthorized users from accessing wireless resources.
- Network Switches and Routers: Securing the devices that manage your network traffic is crucial. Implementing MFA here adds an extra layer of defense against potential breaches.
- Cloud Services: If your organization relies on cloud-based applications or resources authenticated through RADIUS, consider MFA to safeguard cloud access.
- Remote Desktop Services: Protecting remote desktop access with MFA is vital, as it guards against unauthorized remote connections to critical systems.
- Physical Access Control: If RADIUS is used for physical access control systems, MFA can enhance security by requiring multiple authentication factors for building entry.
- Remote Administration: Any remote administration tools or systems leveraging RADIUS should be protected with MFA to prevent unauthorized access to critical network settings.
The scope of RADIUS-enabled devices and services that benefit from Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is broad. By implementing MFA across these key areas, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture, safeguarding their critical assets from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
5. How to Integrate Multi-Factor Authentication for RADIUS Systems
Integrating Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) into RADIUS-supported devices or software is a streamlined process that enhances your network’s security. Here’s a concise guide on how to achieve this integration:
- Registration and Configuration: Begin by either registering with Protectimus SAAS Service or installing the On-Premise 2FA Platform, depending on your organizational needs. Configure the basic settings to align with your security requirements.
- Install Protectimus RADIUS Server: Install and configure the Protectimus RADIUS Server component. This server acts as the intermediary, facilitating the MFA verification process.
- Authentication Request Transmission: Find the necessary integration guidelines within our documentation to enable the transmission of authentication requests over the RADIUS protocol to the Protectimus RADIUS Server and follow the provided instructions. If you don’t find integration instructions for your service, please contact our support team. We will assist you in integrating with virtually any RADIUS-enabled system.
- You can repeat step 3 for as many RADIUS-Compatible services as needed.
Once configured, the Protectimus RADIUS Server component will receive and process the incoming authentication requests from your RADIUS-supported device or software.
By following these straightforward steps, you can implement Multi-Factor Authentication seamlessly into any RADIUS-supported device or software.
6. Understanding Protectimus RADIUS 2FA Solution
The Protectimus two-factor authentication solution for RADIUS offers several unique features and options that enhance the security and flexibility of the authentication process:
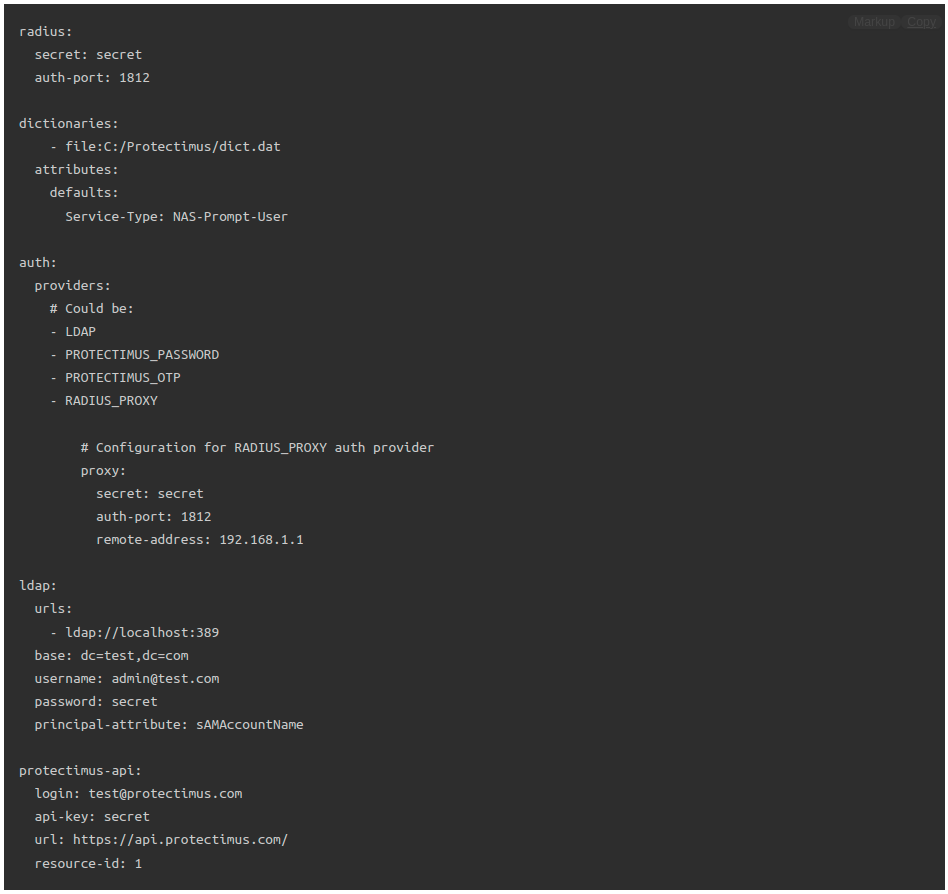
- Comprehensive RADIUS Configuration: Protectimus RADIUS Server allows for extensive configuration options, including setting the RADIUS secret, specifying authentication and accounting ports, defining the server’s listening address, configuring dictionaries for attribute extension, and specifying attributes to be returned on successful authentication. This level of customization ensures compatibility with a wide range of RADIUS-enabled devices and services.
- On-Premise and Cloud Options: Organizations have the choice of deploying the Protectimus two-factor authentication server on-premise or opting for the Cloud MFA Service. This flexibility caters to different deployment preferences and needs.
- Advanced Authentication Settings: The solution offers advanced authentication settings, such as re-entering OTP, principal normalization, and bypassing OTP for specified users. These options enhance security and user experience by tailoring the authentication process to specific needs.
- Advanced LDAP Integration: The solution seamlessly integrates with LDAP for user authentication, enabling organizations to leverage their existing LDAP infrastructure. You can configure LDAP settings, such as the base DN, LDAP server URLs, principal attributes, and custom filters for user access control.
- Inline Mode Support: Inline mode allows for 2FA even when Access-Challenge is not supported. Organizations can activate inline mode and customize the format for password and OTP, increasing compatibility with various systems.
- Dictionary Extension: Protectimus RADIUS Server supports dictionary extensions, allowing organizations to define additional attributes for RADIUS communication, further customizing the authentication process.
- Certification and Compatibility: Protectimus RADIUS 2FA solution is certified by the Initiative for Open Authentication (OATH) and officially recommended for integration with Citrix Gateway, ADC, Virtual Desktops, and Virtual Apps (Citrix Ready). It has a proven track record of reliability and security.
- Advanced two-factor authentication methods: Protectimus offers a diverse range of OATH-compliant two-factor authentication methods to cater to your security needs. These options include classic hardware 2FA tokens like the high-strength and water-resistant OTP tokens Protectimus TWO and Protectimus SHARK, and programmable hardware TOTP tokens like Protectimus Slim NFC Token or Protectimus Flex Token. For those seeking mobile-based solutions, the Protectimus SMART OTP 2FA authenticator app is available for iOS and Android. It offers encrypted cloud backup, PIN, biometric protection, and various customization options. Furthermore, Protectimus offers a cost-effective alternative to SMS authentication with the Protectimus BOT Token, enabling OTP delivery through messaging apps like Telegram, Facebook Messenger, and Viber. For straightforward delivery methods, Protectimus also offers one-time password delivery via SMS messages and email. These diverse authentication methods ensure flexibility and security, making it easy for you to choose the most suitable option for your needs.
These unique features and options make Protectimus RADIUS 2FA a robust and adaptable solution for enhancing the security of RADIUS-enabled devices and services while accommodating various authentication methods and deployment scenarios.
All the integration documentation can be found at this link: https://www.protectimus.com/guides/radius-2fa/. Additionally, our dedicated support team is readily available to assist you in seamlessly integrating two-factor authentication into any situation or infrastructure you may have.
7. Read Also
- Protectimus Customer Stories: 2FA for SICIM
- Protectimus Customer Stories: 2FA for DXC Technology
- Protectimus Customer Stories: 2FA for Advcash
- On-Premise 2FA vs Cloud-Based Authentication
- Protectimus MFA Prices: How to Save with Coupons, Discounts, Referrals, and Subscriptions
- 5 Steps to Prepare your Business for Multifactor Authentication
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.

Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from Protectimus blog.
You have successfully subscribed!