Computer security experts in their confrontation with the hackers are always trying to work ahead of the curve: to model and foresee probable “loopholes” in the data protection systems of different services and operating systems. In recent years, special attention has been paid to the mobile operating systems as more and more people use smartphones to enter their accounts or use them as 2-step verification means. Most often, users get 2-step verification codes (one-time passwords) via SMS. Sometimes, OTP passwords are also delivered via voice messages or generated with the help of a special application – mobile one-time password generator. But in this article, we will discuss the most popular OTP delivery method – SMS verification.
Unfortunately, SMS verification cannot provide a proper level of reliability. First of all, mobile networks use open, unencrypted communication channels where any data protection is almost impossible. It is not difficult for a person who has the necessary technical skills and equipment to get connected to such a network. But, according to the researchers of the Free University of Amsterdam, even this is not so important: they have found another critical vulnerability of the SMS-based authentication.
What is the problem with SMS verification
Usually, a hacker needs two conditions for carrying out two-factor verification on behalf of his victim: a victim’s computer must be infected with the Trojan virus and the hacker should know the static password, which is the first factor of 2-step verification. But the Dutch researchers have found how to intercept the SMS tokens on the mobile devices with Android and iOS operating systems without having a permanent account password.
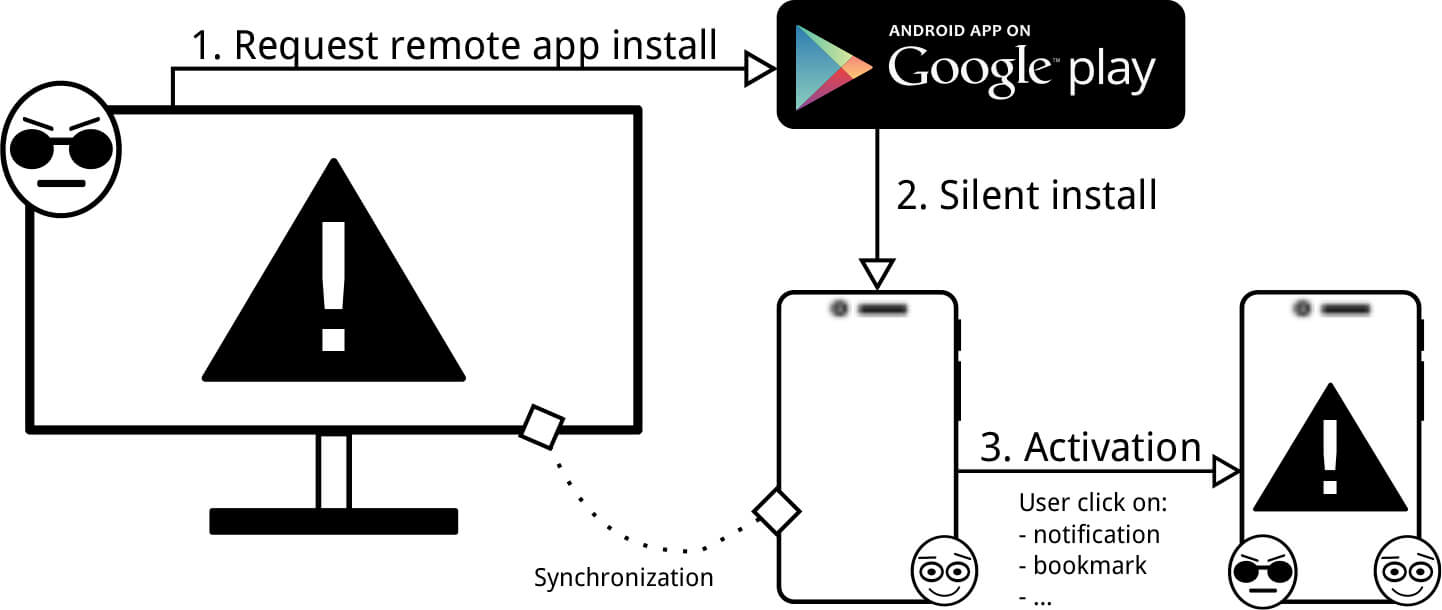
The source of trouble lies in the possibility to synchronize your smartphone and computer. Once invented for convenience, this Apple and Google provided function now can endanger the user’s data protection. Moreover, although earlier the Android operating system was considered the most vulnerable, the present study showed that the vaunted iOS is even easier to hack.
In both cases, the only thing the hacker needs to bypass the SMS-based authentication is to have a victim’s computer infected with the Trojan virus. Usually, it is not difficult to install it: there have already been precedents when the spyware in the guise of the useful programs penetrated to the official app stores. And yes, we shouldn’t forget about phishing, which, despite many warnings, keeps working.
Further events are developing in different ways depending on the operating system – Android or iOS.
In the Android case, the Trojan virus, disguised as the account holder, asks to download a spyware application on your smartphone, connected to the account. Once the malware is installed, it does not manifest itself and waits for an SMS with the OTP password. Then the one-time password is sent to the fraudsters’ server even before the real account holder enters the OTP.
“Working” with OS X and iOS is even easier for the Trojan virus. The latest versions of these operating systems have a feature allowing to read iMessages right from the computer. All incoming messages are placed in a separate file on the computer’s hard drive. The virus only needs to monitor the content in anticipation of the “H-hour.”
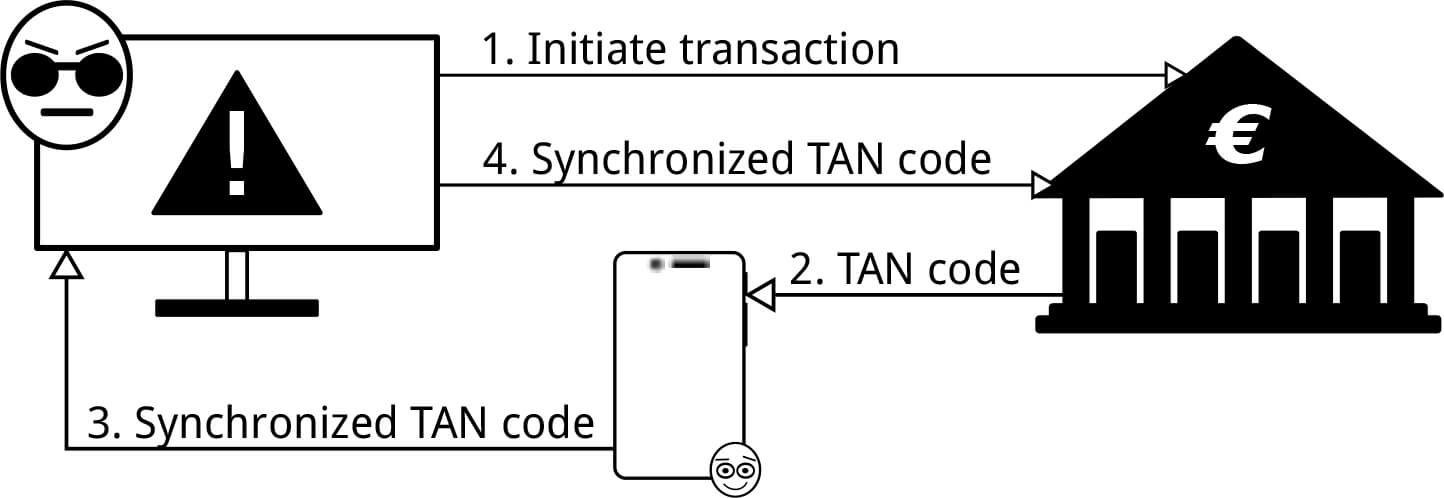
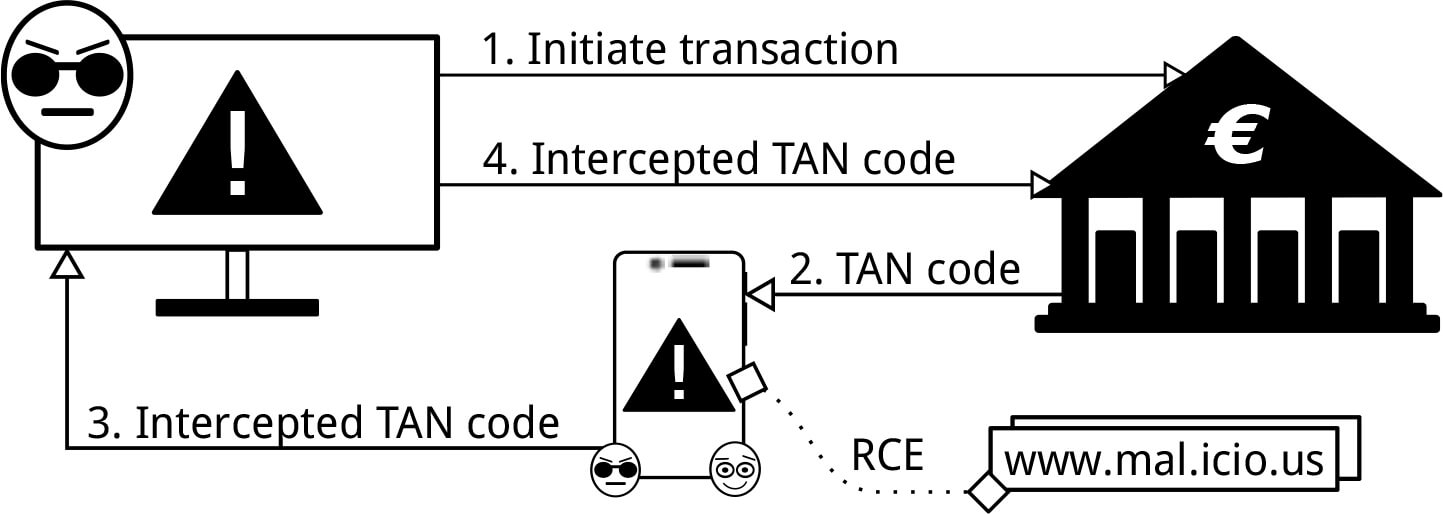
Possible Solution
If the SMS verification can be compromised, what can help you to avoid this threat? Currently, the most obvious solution is hardware OTP token as it can provide the proper security level of the two-factor authentication.
Hardware tokens are the most secure OTP tokens of all the types. This one-time password generator works free of the Internet or GSM network. Moreover, modern hardware tokens can be further protected with the PIN-codes.
When it comes to the usability of tokens, two-factor authentication providers – such as Protectimus – do everything to ensure it to the maximum. Generally, OTP tokens are small and their batteries last for 5 years. Hardware tokens can be made in the form of the key fobs (e.g., Protectimus Ultra and One) or credit cards (Protectimus Slim and Protectimus Slim Mini).
By the way, our new hardware token smart card Protectimus Slim Mini is not only twice smaller than a standard credit card, but it also reprogrammable, supports NFC technology, and allows you to change the lifetime of the OTP password that also increases security.
There are a lot of different authentication methods. But practice shows that one-time password generation with the help of the hardware tokens is the best means to compensate for existing vulnerabilities in 2-step verification.
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.

Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from Protectimus blog.
You have successfully subscribed!